Book An Appointment
Book an online doctor appointment on Dr. Bakshi's Healthcare for expert care anytime, anywhere.
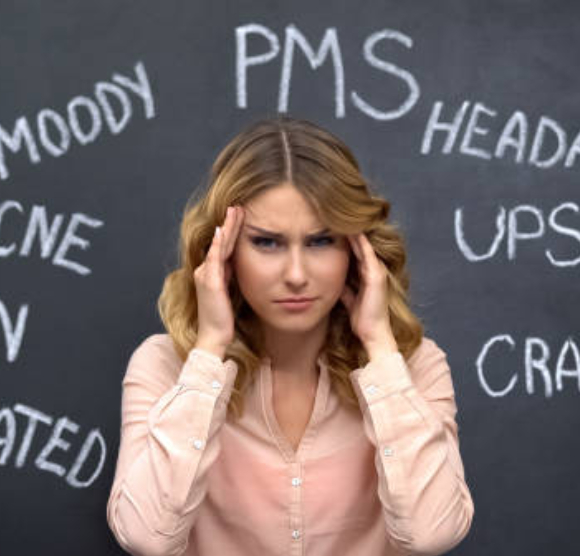
Role of Nutrition
Nutrition and diet are pivotal in the management of hormonal imbalance, as they directly impact the production, regulation, and clearance of hormones from the body. Well-balanced meals are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar and insulin levels, which are critical for the regulation of hormones associated with metabolism, stress, and reproduction. Adequate protein intake is necessary to provide the amino acids required for hormone synthesis, while healthy fats facilitate the production of crucial hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. A diet abundant in fiber enhances gut health and supports liver function, thereby assisting the body in eliminating excess hormones and preventing hormonal overload. Furthermore, essential vitamins and minerals serve as cofactors in hormonal pathways, ensuring appropriate signaling and balance. Conversely, the limitation of refined sugars, processed foods, and trans fats mitigates inflammation and hormonal disruption. In summary, a nutrient-dense, well-structured diet is instrumental in restoring hormonal equilibrium, enhancing energy and mood, and promoting long-term metabolic and reproductive health.
Components of a Healthy Diet
Balanced Macronutrients
Adequate protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to support hormone production and stable blood sugar levels.
High-Fibre Foods
Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes to improve gut health and support the elimination of excess hormones.
Quality Proteins
Lean meats, eggs, dairy, or plant proteins to provide amino acids required for hormone synthesis.
Healthy Fats
Sources like nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish to support the production of reproductive and metabolic hormones.
Micronutrient-Rich Foods
Vitamins and minerals such as B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, and iron that function as cofactors in hormonal pathways.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Fruits and vegetables to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation that can disrupt hormonal balance.
Adequate Hydration
Sufficient water intake to support metabolic processes and hormone transport.
Limited Processed Foods
Reduced intake of refined sugar, trans fats, and highly processed foods to prevent hormonal disruption.
Diet Management
- Follow a balanced diet with adequate protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to support hormone production and stable blood sugar levels.
- Include high-fibre foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes to improve gut health and help eliminate excess hormones.
- Ensure sufficient intake of key micronutrients like B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, and iron, which are essential for hormonal regulation.
- Choose antioxidant-rich foods to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress that can disturb hormonal balance.
- Limit refined sugar, processed foods, excess caffeine, and trans fats, as these can trigger insulin spikes and hormonal disruption.
- Maintain proper hydration to support metabolic and endocrine functions.
Lifestyle Management
- Prioritize regular, good-quality sleep to support cortisol, insulin, and reproductive hormone balance.
- Engage in consistent physical activity, including strength training and moderate cardio, to improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic health.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, breathing exercises, or mindfulness, as chronic stress affects hormone levels.
- Maintain a regular daily routine for meals, sleep, and activity to support circadian rhythm and hormonal stability.
- Avoid smoking, excessive alcohol intake, and sedentary habits, which negatively impact hormonal health.
Our Approach
We focus on correcting underlying nutritional and lifestyle factors that disrupt hormonal regulation, ensuring long-term balance and sustainable health outcomes.

Comprehensive Assessment
Detailed evaluation of age, lifestyle, medical history, symptoms, dietary habits, and hormonal health indicators

Root Cause Identification
Identification of nutritional deficiencies, blood sugar dysregulation, stress-related cortisol imbalance, metabolic issues, and lifestyle factors

Personalized Nutrition Strategy
Development of customized nutrition plans to support hormone production, regulation, and detoxification
Lifestyle Integration
Incorporation of sleep optimization, stress management, physical activity, and daily routine structuring to support endocrine balance
Sustainable Habit Building
Focus on practical, long-term dietary and lifestyle changes that are easy to follow and maintain.

Monitoring and Follow-Up
Continuous monitoring of progress with regular follow-ups and timely plan adjustments to ensure sustained hormonal balance and overall well-being.
Make An Appointment
Have a question or need support?
Share your concerns with us and our experts will help you take the next step toward better health.




